Introduction: AL amyloidosis is characterized by the extracellular deposition of immunoglobulin light chains. Daratumumab is an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody that has demonstrated outstanding results in the treatment of AL amyloidosis, achieving rapid and deep responses and improving OS. Nevertheless, patients with advanced cardiac disease have been usually excluded from clinical trials and data from real world patients in Latin America is lacking. Moreover, subcutaneous Daratumumab is not available in most countries in the region.
Objective: To describe hematological (HR) and organ response, overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) of incorporating IV Daratumumab for the treatment of AL amyloidosis in real world patients from 5 centers in Argentina
Materials and methods: Multicenter, retrospective cohort study of patients older than 18 years with a histopathological diagnosis of AL Amyloidosis and treated with at least one cycle in first-line (Group 1) or subsequent lines of treatment (Group 2) with Daratumumab IV, included in the registry of amyloidosis (RIA, NCT01347047). Data were collected from medical records in an standardized electronic clinical report form (RIA Redcap). The registry includes data for baseline demographics, medical history, comorbidities, physical examinations, laboratory, and imaging exams. Treatments were prescribed by the physician, according to the hospital's protocol. All patients were followed from first daratumumab infusion till death or lost to follow up for HR (as per response criteria by the International Amyloidosis Society, complete response [CR], very good partial response [VGPR], partial response [PR], no response [NR]), OS (time from diagnosis to death), progression free survival (PFS: time from diagnosis to disease progression or death). Adverse events were reported based on CTCAE. Overall and progression-free survival was estimated using Kaplan Meier.
Results
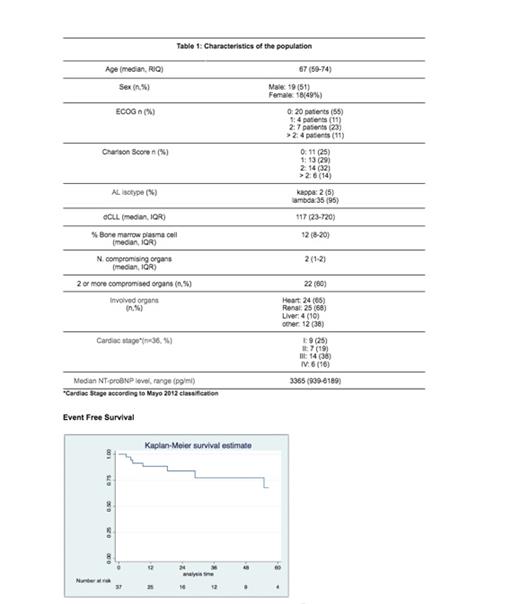
Thirty-seven patients with AL amyloidosis were included in the study. The characteristics of the population are summarized in Table 1. Twenty-four patients (65%) had cardiac involvement, 25 (68%) renal involvement, and 14 (40% ) both. Of the patients with cardiac involvement, 20 had cardiac stages Mayo 2012 III/IV.
Group 1 included 18 patients who received daratumumab (48%), 17 in combination with CyborD. Group 2 included 19 patients (51%), 12 received Daratumumab in combination with dexamethasone, 5 with CyborD and 2 with lenalidomide.
Thirty-three patients (90%) achieved HR, the median time to best hematologic response was 2 months (IQR 1-9 months). Seventeen patients (59%) achieved CR (group1 n=8 Group2 n=9), 9 MBRP (group1 n=4 group2 n=5), 7 PR (group1 n= 5 group2 n=2). Of the 20 patients with Mayo stages III/IV, 18 achieved hematologic response and 9 cardiac response. Three patients had stable disease, all of them were relapsed.. Three patients presented subsequent relapses.
The Organ response rate was 59% (n=22, IC 45-75), 14 renal response, median time to response 8 months (IQ R4,6-14,1), 13 cardiac response, median time to response 6,4 months (IQR 6,4-6,4). Five patients had response of both organs.
The median follow-up of the entire cohort was 18 months (CI 11-75). The median EFS at 1 year was 88% (CI 71-95) and at 2 years 83% (CI 64-93). Median OS at 12 months was 91% (CI 75-97) and at 24 months 86% (CI 68-95). There were 7 deaths in the entire cohort, 5 were due to cardiac complications associated with amyloidosis. Five of the deceased patients had achieved a HR. Eleven patients presented adverse events, mainly infectious complications, 5 of them grade 3 or 4.
Conclusions: This study provides real-world evidence for Daratumumab IV treatment in patients with AL amyloidosis in the first line and at relapse, achieving fast and profound HR, which translated into a high organ response rate and improvement in OS and PFS.
In our cohort, most patients achieved HR with a median time to best response at 2 months consistent with what is reported in the bibliography.
This study is relevant since it is a real life study, in which intravenous daratumumab was used since the subcutaneous formulation is not available in most Latin American countries and also included patients with advanced stages achieving responses in this high risk subgroup.
Treatment with Daratumumab should be considered a therapy of choice in AL amyloidosis, even in patients with advanced cardiac stages.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal